Let’s assume that the exemplary company Grün & Schnabel has sustainability initiatives with an investment volume of some 10 million Euros. It would like to optimize its ESG portfolio (Environment, Social, Government) and prioritize projects according to its corporate goals. In addition, due to its size and location, it is subject to EU taxonomy and must comply with corresponding reporting requirements. The management also aims to actively manage sustainability initiatives based on reliable, up-to-date data.
These ESG initiatives of Grün & Schnabel encompass the following areas:
- reduction of CO2 emissions,
- improving the efficiency of machines and transport,
- employee training programs,
- reducing inequalities such as employee pay,
- supply chain diligence, and
- a sustainable use of water resources
Sustainability Controlling is a responsibility of the controlling department at the Grün & Schnabel company, since the CPM & BI platform (Corporate Performance Management and Business Intelligence) used is from smartPM.solutions and already covers similar tasks in the finance area so that synergies can be used to include sustainability tasks. The implementation of the ESG module was completed very rapidly due to the already existing module content and now releases the controllers from repetitive, manual activities. The modular structure of the smartPM system solutions enabled Sustainability Controlling to be linked to Integrated Financial Planning and other departmental plans. The system was flexibly adapted to the company’s requirements during the implementation, e.g., in terms of the selection of industry specific KPIs and corresponding sub-plans.
SUSTAINABILITY STRATEGY: Which ESG initiatives are to be prioritized? How can I optimize my sustainability portfolio efficiently and easily?
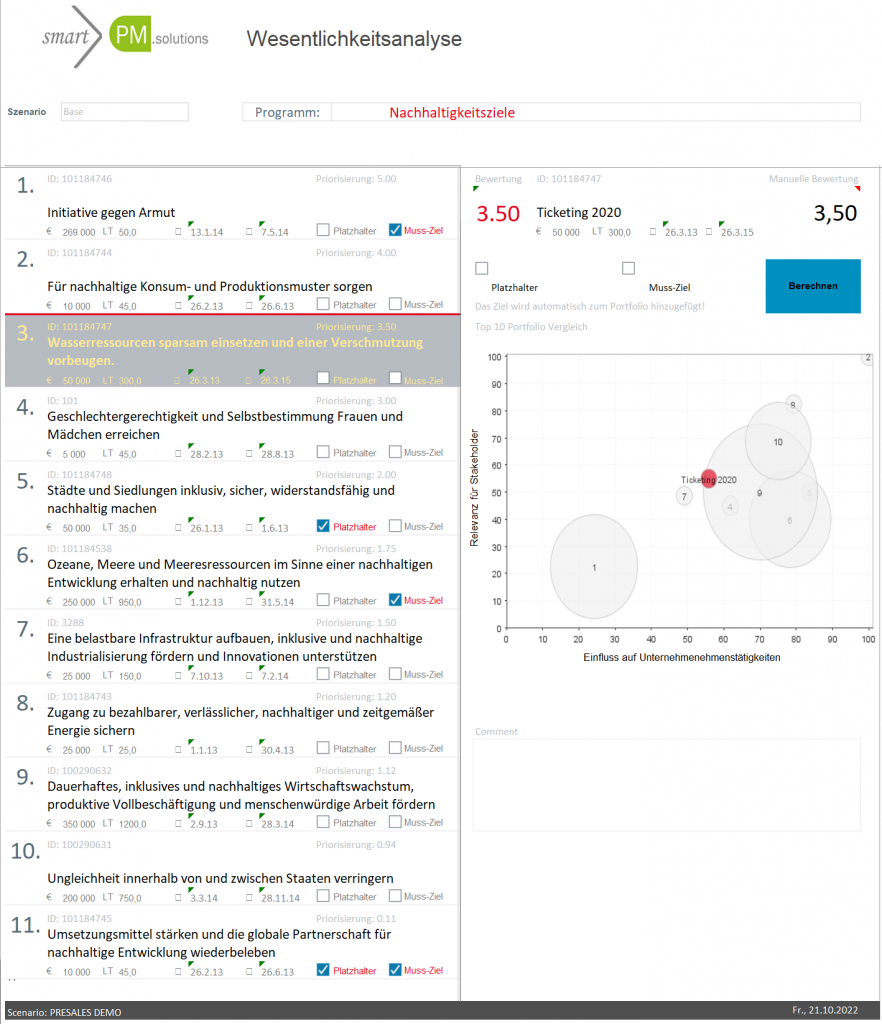
Initially, the controller responsible for sustainability tasks at Grün & Schnabel determined the relevance and prioritization of the initiatives by means of a materiality analysis. This step is already included in the smartPM Sustainability Model and highlights which projects are considered substantial in terms of the corporate strategy and what emphasis they should have in the portfolio. In the dashboard, for example, it is immediately apparent that the CO2 reduction initiative has a high priority from a corporate and stakeholder perspective due to the highest expected investment share.
Is there a standardized way to capture sustainability projects and authorization concepts?
Once the sustainability portfolio has been optimized from a strategic perspective, the next step is the standardized entry of all ESG initiatives in the smartPM Sustainability Controlling system. Here, for example, the start and end dates, investment sums, detailed descriptions, persons responsible, and much more gets recorded in a form. This makes the information comparable and, above all, complete.
NEW WHITEPAPER: Efficient sustainability controlling and simplified reporting: The instructions in 4 steps.
What do I do if management's predetermined sustainability goals deviate from lower-level planning?
Management recently carried out top-down planning for the CO2 reduction sustainability project based on the uniform data platform and compared it with the bottom-up planning of the subordinate levels (regions, plants, etc.) using a countercurrent method. The deviation between the targets is 7.7% and must be closed by further decarbonization measures that are entered into the system. These could include the purchase of e-vehicles, a reduction in business flights, and the expansion of the solar system at the headquarters. All measures require a certain amount of investment and are entered into the system. Without these additional measures, the management targets cannot be achieved.
Monitoring and analysis of sustainability initiatives - leveraging synergies in Controlling
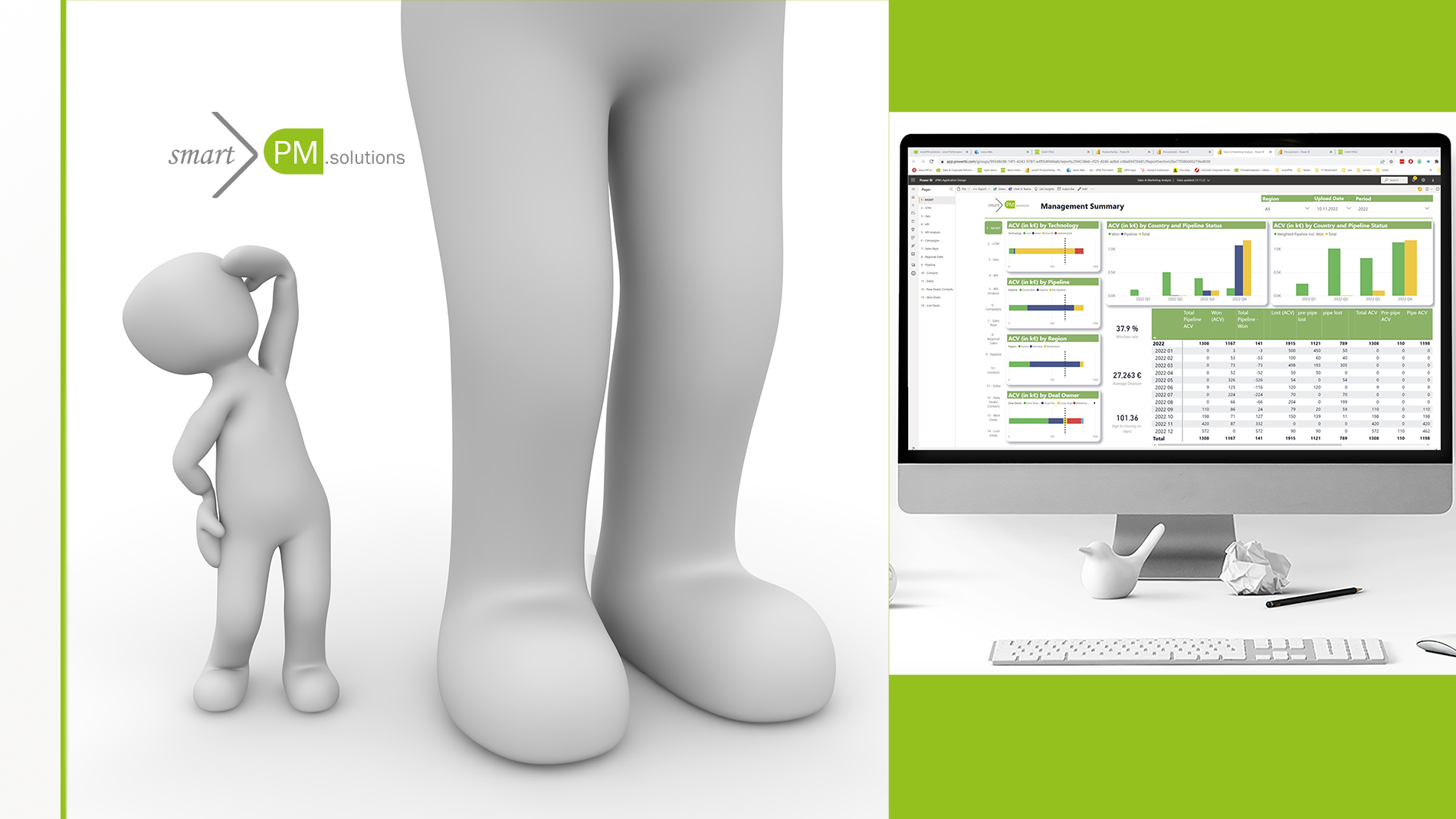
The monitoring and analysis of Grün & Schnabel’s sustainability projects are located in Controlling. Many functions of the Performance Management System can be transferred to Sustainability Controlling tasks. By means of a kick point overview and KPI dashboards, the controller responsible is always informed about all initiatives, their degree of fulfillment and any deviations. At the click of a mouse, they can see that the degree of achievement of the ESG target decarbonization in Phase 3 -“Realization” is currently below the target value and that a longer project duration is likely to be necessary in order to meet the required result. Initiatives are necessary to close this gap. Selected measures, such as the utilization of waste heat are entered in the system, assigned to the parties responsible and then tracked. The controller also notices that the proportion of taxonomy-compliant sustainability initiatives in the ESG dashboard has increased slightly compared to the previous year – which is why he decides to integrate this positive development into the Management Report right away. Authorization concepts secure user access to the data and reports.
How do I design my sustainability reports to be legally compliant, e.g. according to EU taxonomy?
Since our exemplary company Grün & Schnabel is active in the EU and has more than 500 employees, it is subject to the reporting obligations according to EU taxonomy. The required EUT reporting forms are stored in the smartPM system and the reporting template is easily accessible. The information required by the EU on the company and the sustainable corporate and risk strategy are conveniently included in the report.
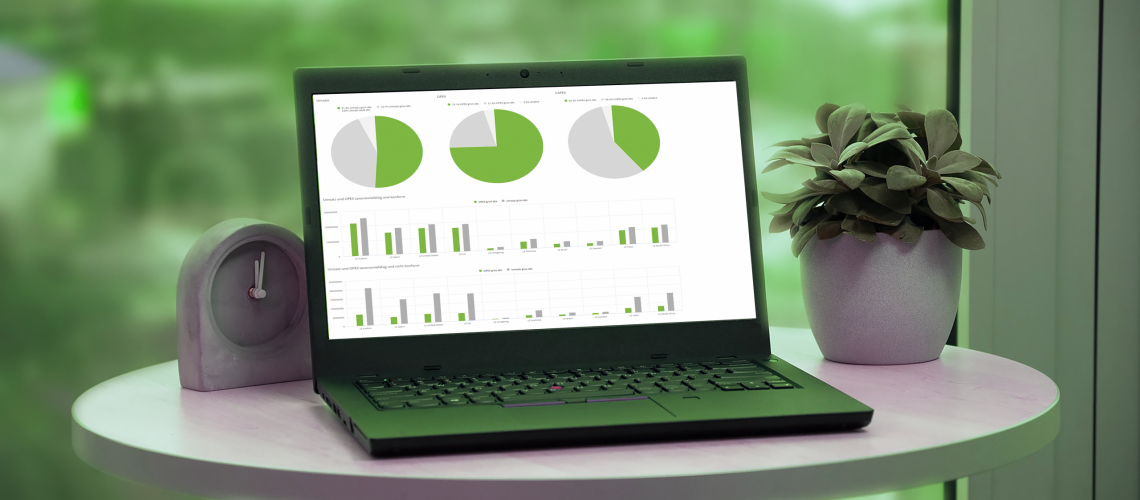
The first point to be addressed is the materiality analysis in alignment with the company’s sustainability strategy. The system supports the presentation of current Sustainability Projects and their development with the automated transfer of figures and dashboards into the report. Well-structured tables present the ESG initiatives divided by OPEX, CAPEX and sales into “green” (taxonomy-capable and compliant), “gray” (taxonomy-capable but non-compliant) and “white” (not EUT-capable) and additionally differentiate by country. The development of CO2 emissions and other sustainability initiatives are presented over time and show target achievement according to business unit. The interdependencies of the sustainability projects can also be analyzed and pinpoint interesting synergy effects between sustainability initiatives.
How can I easily and actively steer ESG initiatives?
The management of Grün & Schnabel has supported the integration of Sustainability Controlling into the Integrated Financial Planning. This allows for scenario comparisons which demonstrate that CO2 reduction as well as the ESG rating have a positive impact on P&L, balance sheet and cash flow as well as bringing a competitive advantage in the young target group. The EBIT margin was increased by 6 percent. In addition, figures from HR show that it is easier to attract new employees as there is a tendency to prefer working for sustainable companies.
At Grün & Schnabel, the Sustainability Report not only serves as a report for the EU, but also supports the management in actively managing corporate sustainability. This starts a cycle of improvements to the sustainability portfolio.